Weightlifting is not just about building muscle and getting stronger. It also has a significant impact on calorie burn and weight loss. Many people wonder how many calories lifting weights can actually burn, and whether it is an effective exercise for reaching their fitness goals.
In this guide, we will explore the mechanics of weightlifting, the science behind it, and its caloric impact. We will also compare weightlifting to cardio exercises, discuss measuring caloric burn during weightlifting, and debunk some common myths. So, if you’re ready to gain a deeper understanding of weightlifting and its calorie-burning potential, keep reading!
Understanding the Mechanics of Weightlifting
Weightlifting, also known as resistance training, focuses on lifting weights to strengthen and condition the body’s muscles. It involves various exercises that target different muscle groups, including the upper body, lower body, and core.

These exercises often use heavy weights and are designed to challenge the muscles, leading to muscle growth and strength development.
By engaging large muscle groups through compound exercises, weightlifting provides a comprehensive workout that can significantly impact overall health and fitness levels.
The Science Behind Weightlifting
The process of resistance exercises places stress on the muscles, stimulating muscle growth and strength. Weight lifting raises the metabolic rate, promoting calorie burn even after the workout.
This type of exercise includes compound movements that target multiple large muscle groups simultaneously, contributing to the development of overall strength. The increase in muscle mass resulting from weight training can support and enhance a weight loss journey by boosting metabolism. Additionally, weightlifting plays a significant role in improving overall health and fitness levels.
Key Components of Weightlifting
When engaging in strength training, the focus is on enhancing muscle strength and mass through targeted exercises for the upper body, lower body, and core muscles. This involves using heavy weights to perform resistance exercises, leading to the development of different muscle groups.

Weight lifting comprises both anaerobic and aerobic exercises, offering a comprehensive way to build muscle. Additionally, it’s worth noting that weight lifting contributes to an increase in calorie intake for muscle gain, highlighting the impact on energy expenditure and the body’s metabolic processes.
The Caloric Impact of Weightlifting
Weightlifting has a significant caloric impact due to the energy expenditure involved in this type of exercise. Strength training, which is a type of exercise that involves anaerobic activity, has been shown to burn more calories than aerobic exercises.
Pound for pound, muscle burns much more energy at rest compared to fat. Additionally, weightlifting helps to increase muscle mass, which can further enhance the amount of energy expended by the body.
Weightlifting and Energy Expenditure
Weightlifting, as a type of exercise, contributes to energy expenditure by increasing calorie burn. This not only impacts body weight and composition but also supports the creation of a calorie deficit, aiding in weight loss.

The resistance exercise involved in weight lifting burns calories, providing much-needed energy. Additionally, muscle gain through strength training elevates the body’s calorie burn, leading to more efficient energy expenditure. Incorporating weightlifting into your fitness routine not only takes less time but also promotes a healthy diet and overall calorie balance.
The Role of Metabolism in Weightlifting
By engaging in strength training, individuals can enhance their metabolic rate, leading to an increase in calorie burn. This type of exercise impacts body mass and strength by building lean muscle mass. Resistance training also supports metabolic health, influencing the number of calories burned.
Additionally, weight lifting sessions have the potential to elevate the body’s metabolic rate, resulting in burning more energy. This proves that weightlifting plays a crucial role in improving metabolism and aiding in calorie burn.
Comparing Weightlifting and Cardio Exercises

Strength training, also known as weightlifting, is an anaerobic exercise that focuses on building muscle strength and endurance. In contrast, cardio exercises such as running or cycling are aerobic, focusing on increasing the heart rate and burning calories.
While cardio may burn more calories during the exercise, strength training continues to burn calories after the workout. Additionally, strength training helps build lean muscle mass, which in turn increases metabolism and burns more calories over time. Both types of exercise have their benefits, and incorporating both into a workout routine can provide a well-rounded approach to fitness.
Calorie Burn: Weightlifting vs. Cardio
When comparing calorie burn, weightlifting and cardio exercise have different impacts on the body. Cardio exercises, such as running or swimming, utilize the aerobic system to burn calories, promoting weight loss.

On the other hand, weightlifting contributes to calorie burn by building lean muscle mass and strength. Combining both types of exercise not only supports overall health but also influences body composition and metabolic rate. Weightlifting and cardio exercises affect energy levels and can be optimized by incorporating light weights and anaerobic exercises.
Which is Better for Weight Loss?
Weight lifting or cardio? Both contribute to weight loss. Weight training supports fat loss, muscle gain, and overall health. Cardio burns calories, enhancing weight loss. Combining both maximizes benefits for calorie burn, body composition, and weight loss journey.
Measuring Caloric Burn During Weightlifting
Measuring the caloric burn during weightlifting is essential to understand the impact of strength training on metabolism.

Unlike aerobic exercises, such as running or cycling, which burn more calories during the activity, weightlifting leads to a higher metabolic rate post-exercise. This is due to the anaerobic nature of strength training, which builds muscle and increases the resting metabolic rate. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends incorporating strength training into a workout routine for overall health and weight management. Utilizing a calorie calculator can help determine the calories burned during weightlifting sessions, complementing a healthy diet for optimal results.
Tools to Measure Calorie Burn
When engaging in strength training, fitness trackers and heart rate monitors can be extremely helpful in tracking calorie burn. Metabolic rate calculators are also useful for estimating the calories burned during this type of anaerobic exercise. Additionally, some weightlifting equipment is designed with built-in calorie tracking features, while smartwatches are able to provide real-time data on calorie burn during weightlifting sessions.

Furthermore, there are various apps and online tools available that offer estimations for the calorie burn associated with different types of weightlifting exercises.
Factors Influencing Caloric Burn in Weightlifting
The calorie burn in weightlifting is influenced by several factors. The amount of weight lifted plays a significant role in determining the calories burned during a weightlifting session.
Additionally, the number of sets and reps, as well as the rest time between sets, affects the total calorie burn. It’s essential to maintain proper form and technique during weightlifting exercises to maximize calorie burn. Moreover, different weightlifting exercises and muscle groups also contribute to varying amounts of calories burned, making it crucial to incorporate a diverse range of exercises for overall calorie expenditure.
The Afterburn Effect in Weightlifting
The afterburn effect, also known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), is the additional calories burned after a workout.

This occurs due to the body restoring itself to pre-exercise levels, and for weightlifting, it can last up to 48 hours. Strength training, a type of anaerobic exercise, leads to EPOC, burning calories even after the workoutThis effect allows for more calories to be burned in less time compared to aerobic exercise.
Additionally, building a pound of muscle consumes much energy, contributing to overall calorie expenditure. The afterburn effect is a key consideration for those looking to optimize their workouts for calorie burn.
What is EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption)?
EPOC, also known as Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption, refers to the increased oxygen intake after intense physical activity. It contributes to additional calorie burn post weightlifting workouts. Understanding EPOC is crucial for optimizing fat loss and overall metabolic impact of weightlifting.
How EPOC Affects Calorie Burn in Weightlifting

Maximizing calorie burn during weightlifting is not just about the workout itself. After completing a weightlifting session, EPOC kicks in, resulting in continued calorie burn. This effect contributes to overall calorie deficit and weight loss, especially from intense weightlifting workouts that can lead to a prolonged EPOC.
Understanding EPOC dynamics is crucial for tailoring weightlifting routines to optimize calorie burn. It influences the total number of calories burned during and after weightlifting exercises, making it an essential factor to consider when aiming for efficient calorie expenditure.
Importance of Weightlifting in a Weight Loss Program
Strength training, a type of exercise that includes weightlifting, is essential for weight loss. It involves anaerobic exercise, which burns more calories than aerobic exercise and helps build muscle.

With strength training, you can achieve results in less time compared to other types of exercise. For every pound of muscle gained, your body burns much more energy, even at rest.
The American College of Sports Medicine recommends incorporating strength training into your fitness routine, alongside a healthy diet, to achieve optimal weight loss results.
Building a Balanced Workout Routine
Building a well-rounded workout routine involves a blend of strength training and aerobic exercise, ensuring comprehensive muscle development. By alternating between various types of strength training, overall muscle growth is promoted, complemented by flexibility and mobility exercises for a balanced regimen.
Prioritizing recovery, rest, and a healthy diet alongside exercise is crucial. Incorporating variety in exercise selection and intensity not only promotes a balanced workout routine but also helps conserve time and energy.
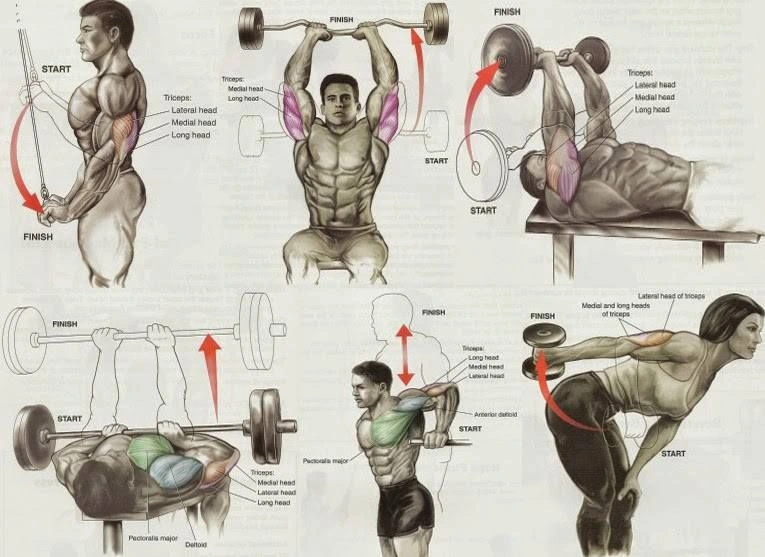
The American College of Sports Medicine suggests integrating a mix of anaerobic and aerobic exercises to maximize calorie burn and muscle gain.
The Role of Diet in Weightlifting and Weight Loss
Proper nutrition is crucial for supporting muscle recovery and growth after weightlifting sessions. Adequate protein intake is essential to facilitate muscle repair and growth, optimizing the benefits of strength training.
Balancing macronutrient consumption plays a vital role in enhancing weightlifting performance and expediting recovery. Adjusting calorie intake based on the intensity and duration of weightlifting sessions can effectively support weight loss goals. Including nutrient-dense foods in a healthy diet provides the energy and essential nutrients required for efficient weightlifting workouts.
Debunking Myths Around Weightlifting

Weightlifting is often associated with bulking up, but it’s a common myth. In reality, strength training helps in toning and defining muscles, not just gaining mass. Additionally, lifting weights doesn’t burn as many calories compared to aerobic exercise, but it increases the resting metabolic rate, leading to more calories burned throughout the day.
This makes weightlifting an essential part of any fitness routine, especially when combined with a healthy diet. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends including strength training exercises in your workout regimen for overall health and fitness benefits.
Weightlifting Leads to Bulking Up: Fact or Fiction?
Weightlifting won’t automatically make you bulky, especially for women. Instead, it focuses on developing lean muscle and toning the body. This myth-busting exercise supports weight loss and body composition goals. Educating individuals about weightlifting helps dispel misconceptions about muscle bulkiness.
Is More Cardio Always Better?

Cardio isn’t the only way to burn calories. Weight training can be just as effective. Not only does it build lean muscle, which increases your metabolic rate, but it also continues to burn calories even after your workout.
So, don’t underestimate the power of lifting weights for calorie burn and overall health.
Starting Your Weightlifting Journey
Embarking on your weightlifting journey contributes to building muscle and supporting weight loss goals.
This type of exercise, known as strength training, offers an excellent way to burn calories and improve body composition. Not only does weight training help in burning calories, but it also aids in building lean muscle mass.
In fact, strength training is an effective way of burning calories and building muscle mass, even after the lifting session ends.

So, next time you hit the gym, consider incorporating anaerobic exercises with light weights into your routine for a more efficient calorie burn.
How Can I Make My Weightlifting Routine More Effective?
Looking to maximize the effectiveness of your weightlifting routine? Incorporate compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Vary your types of exercises to keep your muscles guessing. Target different muscle groups with resistance exercises for increased calorie burn, and focus on large muscle groups during strength training sessions to create a calorie deficit. Utilize isolation exercises to target specific muscle groups, aiding in calorie burn.
Conclusion
In conclusion, weightlifting not only helps in building strength and muscle but also contributes to burning calories. The caloric impact of weightlifting is influenced by various factors such as the intensity and duration of the workout, individual metabolism, and body composition.
While weightlifting may not burn as many calories during the workout as cardio exercises, it has a higher afterburn effect, leading to increased calorie burn even after the workout is over. Incorporating weightlifting into a balanced workout routine and combining it with a healthy diet can be beneficial for both weight loss and overall fitness goals. So, don’t underestimate the power of lifting weights and start your weightlifting journey today!